Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue, as this demographic faces the highest suicide rates across age groups, particularly those aged 75 and older. Studies indicate that while the elderly are significantly at risk, the availability of tailored suicide prevention resources is alarmingly low, leaving many without the help they need. Mental health resources dedicated to older adults are scarce, despite growing awareness surrounding elderly suicide rates and the need for targeted interventions. Healthcare professionals in Geriatric Psychiatry emphasize the urgent requirement for accessible suicide prevention strategies, urging organizations to recognize and address older adults’ unique challenges. By enhancing older adults’ suicide awareness and support systems, we can strive to reduce these tragic rates and foster a healthier, more resilient community among our aging population.
Addressing the issue of suicide among seniors requires comprehensive strategies aimed at enhancing their mental and emotional well-being. The uptick in suicides within this age group highlights an essential need for specialized support systems and resources tailored to their specific mental health challenges. Many older individuals may struggle with feelings of loneliness or social isolation, thereby elevating the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. It is crucial for service providers and caregivers to understand these dynamics and work diligently to develop effective suicide prevention initiatives aimed at seniors. Bridging this gap not only facilitates better outcomes but also fosters a culture of compassion and understanding towards older adults seeking help.
Understanding Elderly Suicide Rates and Their Impact
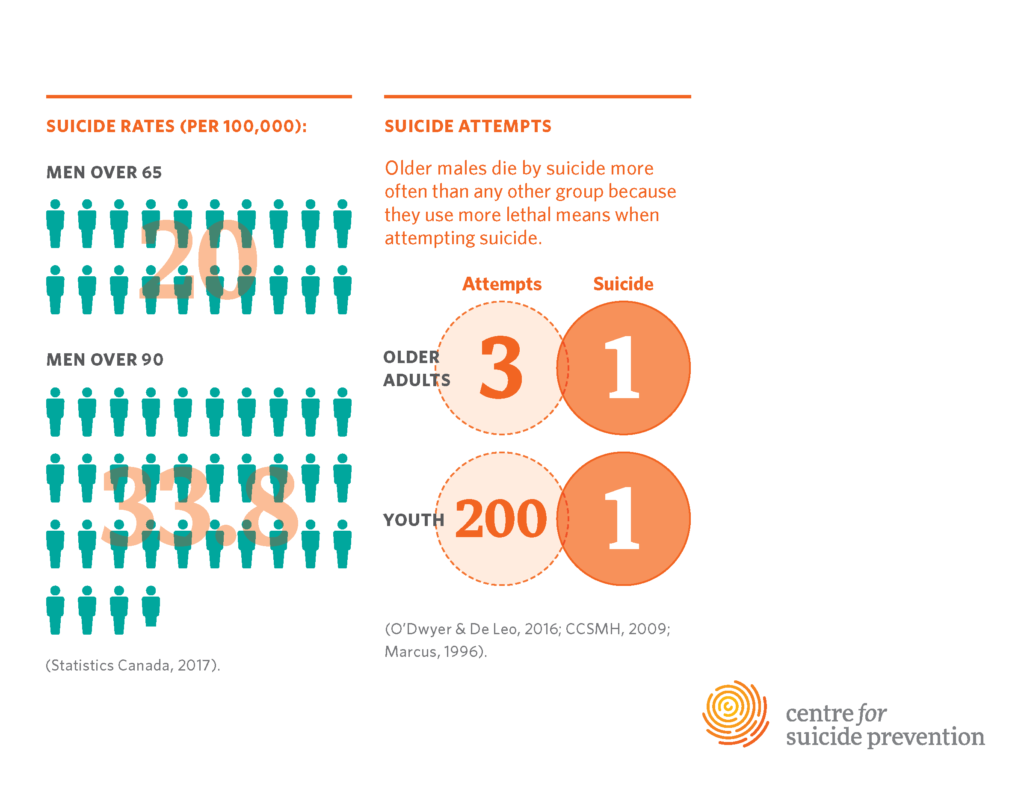
Elderly suicide rates represent a significant public health concern, particularly among those aged 75 and older, who are statistically at the highest risk. Recent studies have shown that this demographic exhibits a suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000 individuals, a figure that starkly contrasts with the declining rates observed in younger populations. Factors contributing to these alarming statistics include social isolation, chronic health conditions, and the mental health stigma that affects older adults disproportionately. This demographic is often overlooked in discussions about mental health, creating an urgent need for targeted awareness and intervention.
Addressing elderly suicide rates requires a multifaceted approach that includes increasing public awareness and enhancing access to mental health resources. Communities must focus on creating supportive environments that mitigate the risks associated with isolation and depression in older adults. By leveraging family involvement and community support systems, it is possible to create a safety net that encourages older adults to seek help and access suicide prevention resources when they need it most.
Essential Mental Health Resources for Seniors
Mental health resources specifically designed for seniors are crucial in addressing the unique needs of this population. Local health departments and community organizations play pivotal roles in providing accessible information about mental health services. However, many older adults may find it challenging to navigate the myriad of resources available to them. Therefore, it is important to streamline these mental health resources, ensuring they are visible and user-friendly for the elderly demographic. Collaborations between mental health providers and community organizations can help improve outreach and facilitate easier access to necessary services.
Telehealth services represent another innovative solution to bridge the gap in providing mental health care for older adults. These platforms enable seniors to access therapy and counseling from the comfort of their homes, breaking down barriers such as mobility issues and transportation challenges. By promoting telehealth practices catered to older adults, mental health professionals can ensure that essential support reaches those who might otherwise remain isolated and without help. Additionally, increasing awareness of these resources within the community can empower older adults to take proactive steps in managing their mental health.
Raising Awareness on Older Adults’ Suicide Prevention
Raising awareness about suicide prevention for older adults is crucial in addressing the rising suicide rates within this demographic. Public campaigns should specifically highlight the signs of suicidal ideation and provide clear information on how families and caregivers can support their elderly loved ones. Initiatives aimed at increasing older adults’ understanding of mental health can foster open conversations about the struggles they face and the resources available to help them cope. By enhancing older adults’ awareness of their own mental health, we create a culture where seeking help is normalized and encouraged.
Moreover, involving older adults in the design and implementation of suicide prevention campaigns can significantly impact their effectiveness. Tailoring messages and strategies according to the lived experiences of seniors contributes to making interventions more relevant and relatable. Community forums, workshops, and support groups facilitated by mental health professionals can serve as platforms to share knowledge and build connections, ultimately reducing the stigma surrounding mental health discussions within the older population.
The Role of Geriatric Psychiatry in Suicide Prevention
Geriatric psychiatry plays an essential role in addressing the mental health needs of older adults, particularly in the context of suicide prevention. This specialty focuses on the complex interplay between aging, chronic illnesses, and psychological well-being, which is critical for delivering effective care to seniors. Professionals in this field are trained to recognize and manage mental health disorders that commonly arise in older adults, such as depression and anxiety, which can increase vulnerability to suicidal behaviors. Their expertise ensures that older patients receive comprehensive evaluations and personalized care plans that address both medical and psychological needs.
Incorporating geriatric psychiatry into healthcare services for older individuals can enhance the identification of at-risk populations and improve outcomes. By promoting collaboration between general practitioners and geriatric psychiatrists, healthcare systems can ensure that seniors receive timely interventions that may prevent suicidal crises. Training programs that enlighten other healthcare providers about the specific symptoms of mental disorders in older adults are necessary to strengthen this approach, creating a more robust safety net that advocates for the mental health of the elderly.
Creating User-Friendly Suicide Prevention Resources
Creating user-friendly suicide prevention resources is critical for making help accessible to older adults. Websites and online platforms need to be designed with the elderly in mind, featuring clear, simple language, and easy navigation. Considering that many older adults rely on the internet for health-related information, it is imperative that suicide prevention organizations invest in developing tailored content that resonates with this audience. Resources can include educational materials, contact numbers for crisis hotlines, and interactive tools that guide users through the process of seeking help.
Moreover, the integration of multimedia elements such as videos and infographics can aid comprehension and engagement among older users. These formats can effectively convey important messages about suicide risk factors, warning signs, and available resources, fostering a sense of connection and understanding. Ensuring that these resources are prominently featured in search engine results will allow older adults to access critical information before they reach a crisis point, serving as a vital step in suicide prevention.
Funding and Research Priorities in Geriatric Suicide Prevention
Increased funding and an emphasis on research priorities regarding geriatric suicide prevention are crucial for addressing this public health issue effectively. Current funding levels for mental health initiatives that focus on older adults are inadequate, limiting the ability to develop comprehensive intervention programs tailored to their unique needs. Advocacy for additional funds from governmental and non-profit organizations will be important in enhancing research initiatives that explore the factors contributing to suicide risk among older individuals and effective prevention strategies.
Research efforts should prioritize understanding the social determinants of mental health in older adults, such as family dynamics, access to care, and life transitions like retirement or the loss of a spouse. By investigating these areas, researchers can identify effective methods for reducing social isolation and enhancing resilience among older populations, ultimately leading to effective suicide prevention strategies. Collaboration between researchers, healthcare professionals, and community leaders is essential to generate actionable insights that can inform policy changes and improve mental health services for the elderly.
The Impact of Isolation on Elderly Mental Health
Isolation is a significant risk factor for mental health issues among older adults, contributing to an increased likelihood of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. The elderly often experience profound loneliness due to life changes such as retirement, loss of loved ones, and declining mobility. As social networks diminish, the mental health ramifications can lead to depression and despair, making it essential to address the impact of isolation as part of any effective suicide prevention strategy. Community programs that promote engagement and encourage regular social interactions can reverse some of these adverse effects.
Creating opportunities for socialization is vital, whether through volunteer programs, community centers, or online platforms tailored to seniors. Engaging in meaningful activities helps build connections and support networks that can alleviate feelings of loneliness. Furthermore, establishing educational workshops that inform older adults about mental health and available resources can empower them and provide strategies to combat isolation in their daily lives. By addressing the root causes of social isolation, communities can improve the overall mental health and well-being of their older members.
How Caregivers Can Support Older Adults in Crisis
Caregivers play an instrumental role in supporting older adults who may be experiencing suicidal thoughts or mental health struggles. Being attuned to the warning signs, such as changes in behavior, withdrawal, or expressions of hopelessness, enables caregivers to approach conversations with empathy and sensitivity. Creating a safe space for communication where older adults feel comfortable sharing their feelings is essential. Caregivers must be equipped with the right knowledge and tools to guide their loved ones towards available resources, including professional help.
Additionally, caregivers should prioritize their well-being as they support older adults. Engaging in self-care practices and seeking support from fellow caregivers or mental health professionals can prevent caregiver burnout, ultimately contributing to a healthier environment for the senior in their care. Ongoing education about mental health issues specific to older adults will further enhance caregivers’ ability to respond effectively to crises and ensure that the elderly receive the compassionate support they need during critical moments.
Leveraging Community Initiatives for Elderly Suicide Prevention
Community initiatives are vital in forming a supportive network for older adults at risk of suicide. Local organizations can implement programs that facilitate access to mental health resources, encouraging open dialogue about mental health issues among seniors. By fostering connections between older adults and local support systems, community initiatives can significantly help reduce feelings of isolation and despair, thereby lowering the risk of suicide. Engaging older adults in the planning of these community programs ensures that the voices of seniors are heard and that services meet their needs effectively.
Moreover, partnerships between healthcare providers, local governments, and non-profit organizations can expand the reach of suicide prevention initiatives. These collaborative efforts provide a broader spectrum of resources and support systems, such as educational workshops, support groups, and helplines tailored to older adults. Promoting awareness of these resources within communities will empower older individuals and their families to take proactive steps towards mental health care, cultivating a culture of compassion and support that can save lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the statistics on elderly suicide rates in older adults?
Elderly suicide rates, particularly among adults aged 75 and older, are notably high, with rates reaching 20.3 per 100,000 individuals according to the CDC. This statistic highlights the critical need for targeted suicide prevention for older adults, as they represent the demographic with the highest risk of suicide.
What mental health resources are available for older adults facing suicidal thoughts?
Mental health resources tailored for older adults include specialized hotlines, therapy providers focusing on geriatric psychiatry, and community support groups. It’s vital for older adults to access these tailored resources to effectively address their mental health needs and reduce the risk of suicide.
How can we improve suicide prevention resources specifically for older adults?
Improving suicide prevention resources for older adults requires the development of user-friendly online platforms and targeted campaigns that resonate with their experiences. Additionally, increasing funding for research in geriatric psychiatry will support customized prevention programs aimed at this vulnerable population.
What is the role of Geriatric Psychiatry in suicide prevention for older adults?
Geriatric Psychiatry plays a crucial role in suicide prevention for older adults by focusing on their unique mental health needs, addressing factors such as social isolation and emotional well-being. Clinicians in this field are trained to recognize and treat suicidal ideation in older adults, thereby contributing to effective prevention strategies.
What efforts are being made to raise older adults suicide awareness?
Efforts to raise awareness about older adults’ suicide include public health campaigns that focus on their specific challenges. These initiatives aim to educate the community, increase understanding of the warning signs of suicide, and promote available mental health resources for this age group.
What are the common factors contributing to suicide risk in older adults?
Common factors contributing to suicide risk in older adults include social isolation, loneliness, chronic health problems, and mental health issues such as depression. Understanding these factors is critical in developing effective suicide prevention strategies that are relevant to older adults.
Why are older adults underrepresented in suicide prevention research?
Older adults are often underrepresented in suicide prevention research due to biases in the healthcare system and a lack of targeted focus on their unique needs. Addressing this gap is essential to create effective interventions tailored to older adults’ mental health challenges.
How can communities support suicide prevention for older adults?
Communities can support suicide prevention for older adults by creating social programs that reduce isolation, fostering intergenerational connections, and ensuring access to mental health resources. Building supportive environments helps empower older adults and enhances their overall well-being.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Risk Age Group | Older adults aged 75 and older have the highest suicide rates. |
| Lack of Resources | Suicide prevention organizations do not provide resources easily accessible to older adults. |
| Research Findings | A study published in The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry highlights a disconnect in online resources for older adults. |
| Factors Affecting Seniors | Social isolation and systemic biases contribute to the rising suicide rates among the elderly. |
| Need for Targeted Campaigns | There is a pressing need for suicide prevention strategies tailored to the healthcare needs of older adults. |
| Future Directions | Calls for increased funding, research, and user-friendly online platforms for older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue that demands immediate attention. With older individuals aged 75 and above experiencing the highest suicide rates and facing significant barriers to accessing necessary resources, it is crucial to implement effective and targeted prevention strategies. The findings of recent studies underscore the urgent need for healthcare initiatives that cater specifically to the elderly population, addressing factors such as social isolation and the underrepresentation of older adults in mental health research. By improving accessibility and tailoring campaigns, we can better support older adults in overcoming the challenges they face regarding mental health and well-being.