Age-related brain diseases such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression are significant health challenges that escalate with advancing years. Recent research has identified 17 modifiable risk factors that can lower the incidence of these debilitating conditions. By focusing on blood pressure, kidney health, physical activity, and other lifestyle choices, individuals can effectively enhance their brain health and reduce the likelihood of developing these diseases. Moreover, understanding and modifying these risk factors for dementia not only aids in preventing stroke but also plays a crucial role in the mental well-being of older adults. As awareness grows, simple lifestyle adjustments can pave the way for healthier aging and improve the quality of life for senior populations.
Age-related cognitive decline manifests in various forms, including strokes, memory impairments, and emotional disturbances commonly seen as late-life depression. These conditions often share overlapping contributing factors, making the pursuit of better brain health a multifaceted approach. Understanding the dynamics of how certain lifestyle choices influence the risk of these age-related brain afflictions is essential. Researchers have explored preventative strategies that emphasize lifestyle modifications, highlighting the significance of factors such as dietary habits and social engagement. As the aging population continues to grow, prioritizing cognitive health and mental wellness has never been more vital.
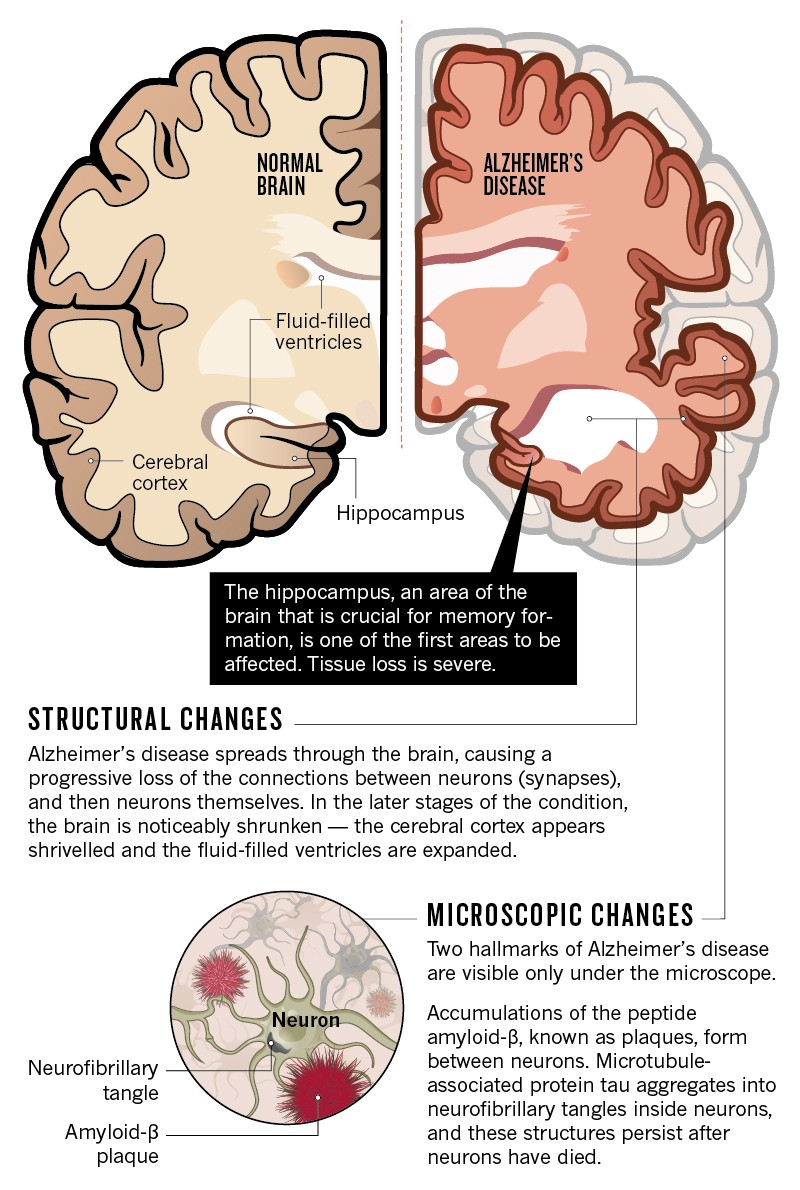
Understanding Age-Related Brain Diseases
Age-related brain diseases, including dementia and stroke, represent a significant health concern as populations age. The interconnectedness of these conditions makes it imperative to understand the underlying risk factors that contribute to their development. Researchers at Mass General Brigham have found that addressing modifiable factors can greatly reduce the incidence of these diseases, highlighting the role lifestyle choices play in maintaining optimal brain health.
By recognizing and modifying risk factors such as high blood pressure, poor diet, and lack of physical activity, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their cognitive function and overall wellbeing. Additionally, the study indicates that late-life depression is often comorbid with dementia and stroke, further emphasizing the importance of comprehensive health strategies to manage these intertwined issues.
Top Risk Factors for Dementia and Stroke
The research identified 17 shared risk factors that significantly increase the likelihood of developing age-related brain diseases. Key among these factors are conditions like hypertension and high cholesterol levels, which have substantial impacts on brain health. These findings underscore the importance of regular health screenings and lifestyle adjustments to manage blood pressure and lipid levels, as such changes can mitigate the risk of stroke and cognitive decline.
In addition to physiological factors, lifestyle choices related to diet, alcohol consumption, and physical activity are also critical in the prevention of dementia and stroke. Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains not only improves general health but can also lower the risk of developing these debilitating conditions, making awareness and education vital in communities.
Modifying Risk Factors to Enhance Brain Health
The study’s findings reveal that modifying even one of the identified risk factors can lead to a significant reduction in the risk of stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. Simple lifestyle modifications, such as increasing physical activity and enhancing dietary habits, can yield substantial benefits for brain health. Engaging in regular exercise has been shown to improve cardiovascular health, which in turn benefits cognitive function.
Moreover, maintaining social engagement and pursuing hobbies can help stave off depression, further illustrating the interconnected nature of these health issues. By prioritizing mental and physical health, individuals can take proactive steps toward preventing diseases that are often linked with aging, reinforcing the idea that brain health is integral to overall quality of life.
The Role of Late-Life Depression in Brain Diseases
Late-life depression has emerged as a significant risk factor for both dementia and stroke, showcasing the complex interplay between mental health and cognitive function. The presence of depression can exacerbate the decline in cognitive abilities, leading to a vicious cycle that can be challenging to break. Thus, addressing mental health issues in older adults is crucial for preventing the onset of more severe neurological conditions.
Effective interventions aimed at reducing the symptoms of late-life depression may not only enhance the quality of life for affected individuals but could also lower the risk of developing associated brain diseases. Therefore, it is essential for healthcare providers to recognize the signs of depression and implement treatment strategies that might prevent further cognitive decline.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Cognitive Function
Lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in determining an individual’s risk profile for age-related brain diseases. The study emphasizes activities such as regular physical exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate social engagement as fundamental for maintaining cognitive health. Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, like puzzles or reading, can also have protective effects on brain function.
Furthermore, reducing sedentary behavior and incorporating more movement throughout the day can help combat both obesity and cardiovascular issues that contribute to brain diseases. By making conscious choices that prioritize physical and cognitive activity, individuals can significantly enhance their brain health as they age.
Preventing Stroke Through Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing strokes is possible through lifestyle modifications that target identified risk factors. High blood pressure management and maintaining healthy cholesterol levels are critical components in reducing stroke risk. By adhering to regular exercise routines and proper nutrition, individuals can significantly improve their cardiovascular health, thereby protecting their brain.
Moreover, reducing alcohol intake and avoiding smoking are vital strategies for stroke prevention. As these factors contribute to the overall health deterioration, addressing them can lead to improved outcomes for cardiovascular and cognitive function, ultimately lowering the incidence of stroke.
Dietary Influence on Brain Health
Diet plays a crucial role in brain health, and the study reveals that poor dietary habits are a formidable risk factor for age-related brain diseases. Diets high in saturated fats, sugars, and processed foods can exacerbate conditions like obesity and hypertension, both of which are linked to increased dementia risk. Instead, focusing on a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and healthy fats can promote cognitive health.
Families and communities should emphasize healthy eating as a preventive strategy against brain diseases. Educational programs can facilitate better understanding of nutrition and its implications for mental health, enriching the lives of older adults and potentially safeguarding them against dementia and stroke.
The Importance of Social Engagement for Older Adults
Social engagement is crucial for older adults, as it combats loneliness and fosters mental well-being. The study identified insufficient social interaction as a significant risk factor for depression and related brain diseases. Maintaining relationships and participating in social activities can enhance quality of life and reduce feelings of isolation that often accompany aging.
Encouraging social engagement within communities can provide a buffer against cognitive decline, emphasizing the necessity of creating environments where older adults feel valued and connected. Programs that promote group activities, thus reinforcing social ties, are instrumental in supporting mental health.
Future Directions for Research in Brain Health
The findings from the Mass General Brigham study open avenues for further research in the realm of brain health. Continued examination of modifiable risk factors, especially in the context of different population demographics, can yield vital insights into effective prevention strategies for age-related diseases. A focus on randomized controlled trials utilizing tools like the Brain Care Score could offer actionable guidelines for healthcare providers.
Additionally, understanding the interaction between various risk factors and how they compound effects over time can pave the way for personalized interventions. As research evolves, the integration of practical health applications highlighting the importance of lifestyle choices can galvanize public engagement in maintaining brain health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key risk factors for dementia and age-related brain diseases?
The study identified 17 modifiable risk factors for dementia and age-related brain diseases, including high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, poor diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, and chronic stress. Modifying any of these factors can help lower the risk.
How can I prevent stroke and age-related brain diseases?
Preventing stroke and age-related brain diseases involves addressing modifiable risk factors like controlling blood pressure, maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, staying physically active, and reducing alcohol consumption. Lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk.
What role does diet play in preventing age-related brain diseases?
A healthy diet is crucial for preventing age-related brain diseases. Poor dietary habits can increase the risk of stroke, dementia, and depression. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can greatly benefit brain health.
Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of late-life depression associated with brain diseases?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as regular physical activity, social engagement, and maintaining a sense of purpose can help reduce the risk of late-life depression. Addressing these modifiable risk factors is important for brain health.
How does social engagement impact the risk of dementia and other age-related brain diseases?
Insufficient social engagement has been linked to an increased risk of depression and dementia. Staying socially active may help mitigate these risks and promote better brain health as you age.
What is the Brain Care Score and how does it relate to age-related brain diseases?
The Brain Care Score is a tool developed by researchers to measure efforts in protecting brain health. It incorporates knowledge of modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases, guiding individuals on how to improve their brain health.
Are there specific strategies for modifying risk factors for dementia?
Yes, strategies for modifying risk factors for dementia include adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical exercise, managing stress, and participating in social activities. These lifestyle adjustments can significantly decrease dementia risk.
What connection exists between stroke, dementia, and late-life depression?
Stroke, dementia, and late-life depression are interconnected, with overlapping risk factors. Developing one can increase the likelihood of facing another, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures for all three conditions.
How does physical activity influence brain health in older adults?
Physical activity is a vital modifiable risk factor that can lower the risk of age-related brain diseases like dementia and stroke. Regular exercise enhances brain health by improving blood flow and cognitive function.
What should I do if I am concerned about my risk for age-related brain diseases?
If you’re concerned about your risk for age-related brain diseases, consult a healthcare provider who can review your medical history and help you address modifiable risk factors through lifestyle changes and regular health check-ups.
| Risk Factor | Associated Conditions | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Moderate to High |
| Blood Pressure | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | High |
| Kidney Disease | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | High |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | Stroke, Dementia | Moderate |
| Total Cholesterol | Stroke, Dementia | Moderate |
| Alcohol Use | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Moderate to High |
| Diet | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Moderate |
| Hearing Loss | Dementia | Moderate |
| Pain | Depression | Moderate |
| Physical Activity | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Moderate to High |
| Purpose in Life | Depression | Moderate |
| Sleep | Depression | Moderate |
| Smoking | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | High |
| Social Engagement | Depression | Moderate |
| Stress | Depression | Moderate to High |
| Obesity | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Moderate |
Summary
Age-related brain diseases, including stroke, dementia, and depression, pose significant health concerns as populations age. Recent research has uncovered 17 modifiable risk factors that individuals can address to lower their risk for these conditions. These factors, ranging from blood pressure management to lifestyle changes such as increased physical activity and better diet, highlight the interconnectedness of these diseases. By focusing on prevention through the modification of these risk factors, there exists a promising opportunity to reduce the prevalence of age-related brain diseases and enhance overall brain health.