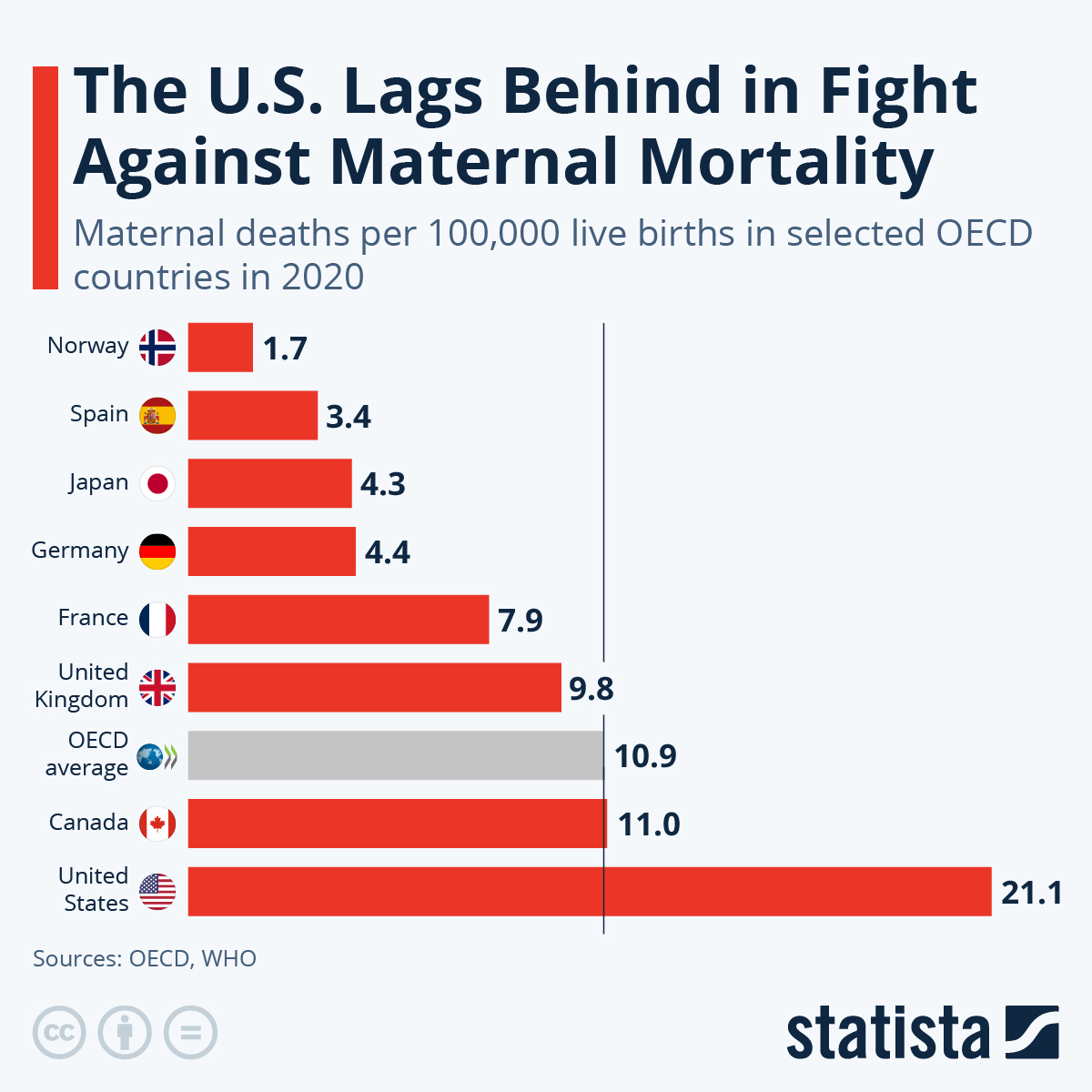
Maternal mortality rates in the United States remain alarmingly high, particularly when compared to peer nations. Research indicates that most of these pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, underscoring critical gaps in maternal health care across the country. From 2018 to 2022, an increasing trend in mortality rates has been observed, showcasing significant disparities linked to race and ethnicity. High-risk pregnancies, combined with insufficient postpartum care, contribute to these dire statistics, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive public health infrastructure. Addressing maternal health disparities through improved access and policies is essential to reversing this troubling trend and ensuring safer outcomes for mothers and babies alike.
The issue of maternal mortality encompasses a range of terms and concepts, often referred to as pregnancy-related deaths and the associated risks faced by vulnerable populations. This pressing matter addresses not only the loss of life but also the health inequities that result in severe outcomes for many women during and after childbirth. By examining the landscape of maternity care, it becomes evident that enhanced postpartum assistance and effective management of high-risk pregnancies are crucial. Moreover, investing in robust public health systems and targeted interventions can bridge the existing maternal health disparities prevalent across different demographics. Ultimately, acknowledging and addressing these critical challenges is imperative for safeguarding the lives of mothers in the United States.
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. have emerged as a significant public health concern. With over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths deemed preventable, the high numbers indicate systemic flaws within the healthcare framework. The latest statistics from a recent study illuminate that the U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality, a disturbing trend persisting for many years. Issues such as the inequitable distribution of healthcare facilities, differing state policies, and societal biases contribute to these alarming figures. For instance, research highlights that, while the national rate of 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births may appear understated, it masks vast disparities faced by specific groups, particularly racial minorities.
Moreover, the rising trends in maternal mortality rates can partly be attributed to enhanced awareness and reporting systems that were established only recently. The CDC’s data indicates a noticeable increase in pregnancy-related deaths, particularly amidst the backdrop of the COVID-19 pandemic. Racial disparities are stark; American Indian and Alaska Native women bear the brunt with nearly four times the mortality rate compared to their white counterparts. Understanding the reasons behind these statistics, alongside proactive measures to address them, is paramount for improving overall maternal health outcomes in the U.S.
The Role of Postpartum Care in Maternal Health
Postpartum care is a vital aspect of maternal health that significantly influences long-term well-being for new mothers. The traditional model tends to focus excessively on the immediate weeks following childbirth, neglecting the subsequent months crucial for recovery. Recent findings indicated that late maternal deaths—those occurring between 42 days to one year post-birth—accounted for nearly one-third of all maternal deaths in the U.S. This prompts a reevaluation of the healthcare system’s approach to postpartum care, advocating for a more comprehensive support structure that addresses the intricate needs of mothers well beyond the early weeks.
Strengthening postpartum care is essential not only for reducing mortality rates but also for mitigating maternal health disparities. Proper postpartum support, including access to mental health services and ongoing evaluations for pre-existing conditions, can help in recognizing and addressing complications early. Healthcare systems need to be redesigned to provide continuous care and support, forming a continuum that extends beyond the conventional six weeks, thus improving the overall quality of maternal health care.
Addressing Maternal Health Disparities
Maternal health disparities remain rife across the United States, with stark differences in outcomes based on race, ethnicity, and geographic location. American Indian, Alaska Native, and non-Hispanic Black women face disproportionately high rates of pregnancy-related deaths. Such disparities illustrate the urgent need for healthcare reforms that focus on equity, ensuring that all women, regardless of their background, have access to high-quality maternal care. The consistency of these findings underscores a systemic problem, one that calls for immediate intervention and targeted policy changes.
Efforts to rectify maternal health disparities must include a commitment to addressing the social determinants of health, such as education, income, and healthcare accessibility. Public health initiatives should aim to dismantle biases and promote inclusive practices within the healthcare system. By fostering a healthcare environment that recognizes and actively mitigates these disparities, we can take significant steps toward improving maternal health outcomes for all populations, ultimately contributing to a decrease in overall maternal mortality rates.
The Impact of High-Risk Pregnancies on Maternal Mortality
High-risk pregnancies are a prominent contributing factor to increased maternal mortality rates. Conditions such as pre-existing hypertension, diabetes, and advanced maternal age elevate the risk of complications, requiring tailored medical attention and management strategies. It is crucial that healthcare providers identify pregnancies that fall into the high-risk category early on, ensuring that appropriate interventions and monitoring practices are in place to mitigate risks associated with these pregnancies.
For women with high-risk pregnancies, effective prenatal care and personalized birthing plans are essential for preventing adverse outcomes. This may involve interdisciplinary care approaches, including consultations with specialists to address emerging complications. By prioritizing high-risk pregnancies and implementing comprehensive care strategies, healthcare systems can work towards reducing pregnancy-related deaths and improving maternal health for vulnerable populations.
Enhancing Public Health Infrastructure for Maternal Care
A resilient public health infrastructure is foundational to combating the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. Current evidence suggests that the country’s fragmented healthcare system undermines cohesive approaches to maternal health. Investing in infrastructure that facilitates better data tracking, coordination of care, and community outreach is critical. Strengthening these elements can ensure that healthcare disparities are addressed and allow for responsive adjustments to policies affecting maternal health outcomes.
Moreover, federal and state-level investments must be prioritized to develop innovative solutions aimed at enhancing the quality of postpartum care and overall maternal health. Allocating resources towards education and training for healthcare providers, alongside public health campaigns focused on awareness and prevention, can cultivate an informed populace that prioritizes maternal health. Together, these efforts will fortify the infrastructure necessary for safeguarding the health of mothers and ensuring equitable health care access.
The Importance of Cardiovascular Health in Pregnancy
Cardiovascular health is a critical component of maternal health, particularly given the recent statistics revealing a shift towards cardiovascular conditions as leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. Factors such as obesity, chronic hypertension, and other pre-existing heart conditions can complicate pregnancies and contribute to adverse health outcomes. Focusing on cardiovascular health before and during pregnancy has the potential to reduce these risks significantly, thereby decreasing maternal mortality rates.
Educational initiatives aimed at pregnant women regarding cardiovascular risks can empower them to seek appropriate care and make healthier lifestyle choices. Regular screenings and monitoring of cardiovascular health during and beyond pregnancy are necessary for early intervention. By emphasizing the importance of managing cardiovascular health, healthcare providers can support mothers in navigating their pregnancies safely, ultimately enhancing maternal well-being and reducing associated mortality.
Integrating Policy Reforms to Improve Maternal Health
Policy reforms play a pivotal role in shaping maternal health outcomes across the United States. Disparities in maternal mortality are influenced by varying state policies, healthcare access, and funding allocations. Addressing these factors involves creating comprehensive strategies that facilitate equitable healthcare access for all women, especially marginalized populations who face systemic barriers. Investments in high-quality maternal care, alongside robust public health policies, are essential for systemic changes that promote overall maternal health.
Moreover, it is crucial to engage community stakeholders in the dialogue surrounding maternal health policies. By prioritizing the voices and needs of the communities most affected by maternal health disparities, policymakers can ensure that interventions are both relevant and effective. Collaboration between public health professionals, practitioners, and community leaders can foster innovative solutions that target the root causes of maternal mortality and enhance the overall quality of care for all mothers.
The Importance of Prenatal Care in Reducing Deaths
Prenatal care is a cornerstone of ensuring healthy pregnancies and reducing maternal mortality rates. By providing expectant mothers with regular check-ups and screenings, healthcare providers can monitor both maternal and fetal health closely. Early identification of potential complications allows for timely interventions and tailored care plans that are crucial in managing high-risk pregnancies. Without adequate prenatal care, many women are at increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes, including pregnancy-related deaths.
Access to comprehensive prenatal care ought to be recognized as a right for all women, facilitating education on maternal health while ensuring that consistent support is provided throughout the pregnancy. Community health programs that focus on outreach and education can empower women to seek the necessary care. Fostering environments where women feel supported and informed about their health can significantly reduce rates of preventable pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.
Future Directions for Maternal Health Advocacy
The landscape of maternal health in the U.S. necessitates a robust commitment from various stakeholders to drive meaningful progress against rising maternal mortality rates. Advocacy for maternal health must engage a multifaceted approach, mobilizing efforts from health professionals, communities, and policymakers alike. Investing in education and awareness initiatives will help to create an informed public that prioritizes maternal health, while data collection and analysis can inform strategies for effective interventions.
Furthermore, collaboration among organizations focused on maternal health can amplify efforts to address systemic issues leading to health disparities. By joining forces, various stakeholders can develop targeted educational resources and advocacy tools aimed at improving maternal care. As the conversation around maternal health continues to evolve, elevating the experiences of diverse populations will be crucial in shaping policies that foster health equity and lower the rates of pregnancy-related deaths across the nation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
The main causes of maternal mortality rates in the U.S. include cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, and other pregnancy-related complications. A significant portion of these deaths are preventable with proper prenatal and postpartum care, highlighting the need for improvements in maternal health services.
How do racial and ethnic disparities affect maternal mortality rates?
Racial and ethnic disparities significantly affect maternal mortality rates. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience the highest rates, nearly four times higher than white women. These disparities reflect ongoing inequities in healthcare access and quality, necessitating targeted interventions to bridge these gaps.
What role does public health infrastructure play in addressing maternal mortality rates?
Public health infrastructure is crucial for addressing maternal mortality rates. Improved data collection, healthcare access, and support systems are essential for monitoring and reducing these rates. Investing in public health can lead to more effective policies and practices that improve maternal health outcomes across communities.
Why is extended postpartum care important for reducing pregnancy-related deaths?
Extended postpartum care is vital as nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths, termed ‘late maternal deaths,’ occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. This suggests that continuous care beyond the immediate postpartum period is necessary to address complications and improve maternal health outcomes over time.
What innovations are being explored to combat maternal health disparities?
Innovations aimed at combating maternal health disparities include implementing better prenatal care models, enhancing community health support, and tailoring interventions to high-risk pregnancies. By focusing on preventive care and addressing root causes of disparities, these innovations can significantly reduce maternal mortality rates.
How can states improve their maternal mortality rates to match better-performing states?
States can improve their maternal mortality rates by investing in quality maternal healthcare, enhancing public health policies, and providing comprehensive support systems. By analyzing successful practices from states like California, other states can adopt evidence-based strategies to improve outcomes and reduce disparities.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on maternal mortality rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on maternal mortality rates, with a sharp increase observed in 2021. The pandemic exacerbated existing health disparities and highlighted the vulnerabilities of the maternal healthcare system, necessitating a critical reevaluation of care practices and policies.
What actions can be taken to prevent pregnancy-related deaths?
To prevent pregnancy-related deaths, it is essential to improve access to quality maternal healthcare, enhance prenatal and postpartum support services, and address systemic inequalities in healthcare. Advocacy for policy changes and increased funding for maternal health initiatives is also crucial in driving improvements in this area.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Trends | U.S. maternal mortality rates are rising, reaching 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, up from 25.3 in 2018. |
| Preventable Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| Disparities in Mortality Rates | Significant disparities exist across racial groups, with American Indian and Alaska Native women having the highest rates. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The most significant increase in maternal deaths occurred in 2021, coinciding with the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Chronic Health Issues | An increase in chronic conditions like hypertension among younger individuals is contributing to rising maternal mortality. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days to 1 year postpartum, indicating a need for continuous care. |
| Challenges in Data Tracking | Inconsistent tracking of maternal deaths until 2018 has complicated understanding and addressing the mortality rates. |
| Policy Recommendations | To improve outcomes, investments in public health and innovative healthcare solutions during pregnancy and postpartum care are essential. |
Summary
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. remain alarmingly high, with the country leading among high-income nations in such deaths. Despite more than 80% of these deaths being preventable, systemic issues within healthcare, disparities across racial groups, and insufficient postpartum care persist. Comprehensive reforms are urgently needed to address these factors, enhance prenatal and postpartum care, and ultimately reduce maternal mortality rates.